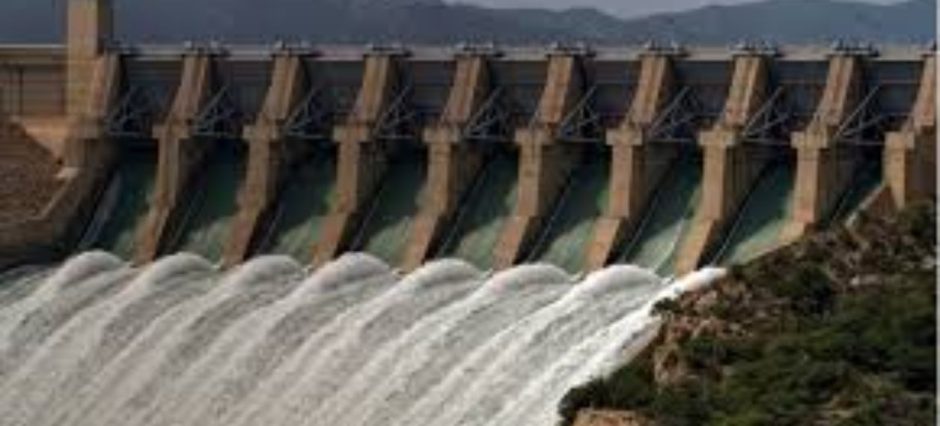
The Tarbela Dam is one of Pakistan’s greatest engineering achievements. It stands on the mighty Indus River in the Haripur District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. As the world’s largest earth-filled dam, it plays a vital role in the country’s water storage, electricity generation, and flood control systems.
Built to meet Pakistan’s growing need for irrigation water and power, Tarbela Dam has become a symbol of progress, technology, and national development. It continues to support millions of people by providing water, energy, and protection from floods.
History and Background of Tarbela Dam
The Tarbela Dam project began after Pakistan faced serious water challenges following independence. The 1960 Indus Waters Treaty between India and Pakistan allowed Pakistan to use the Indus River and its western tributaries. To manage this resource effectively, the government decided to build large dams.
Construction of Tarbela Dam started in 1968 with help from international engineers and financial support from the World Bank. It took almost eight years to complete, and the dam officially began operation in 1976.
Since then, several expansion and upgrade projects have been carried out to increase its power generation capacity and improve efficiency.
Location and Structure
The Tarbela Dam is built on the Indus River, about 50 kilometers northwest of Islamabad. It is located near the town of Tarbela, close to Haripur.
The dam is an earth and rock-filled structure with a height of around 485 feet (148 meters) and a length of about 9,000 feet (2,743 meters). Its reservoir covers a large area, capable of storing more than 11 million acre-feet (MAF) of water.
This huge storage capacity makes Tarbela Dam one of the most important water reservoirs in South Asia.
Purpose and Main Functions
The Tarbela Dam was designed with multiple purposes in mind. Its main goals include:
- Irrigation: Supplying water to Pakistan’s vast agricultural lands.
- Hydropower Generation: Producing clean and renewable electricity.
- Flood Control: Managing heavy river flows during monsoon seasons.
These three functions make the dam a critical part of Pakistan’s water and energy infrastructure.
Hydropower Generation
The Tarbela Hydropower Plant is one of the largest in the world. It generates over 4,800 megawatts (MW) of electricity, which meets a major portion of Pakistan’s energy needs.
The dam’s powerhouse has multiple tunnels and turbines that convert the flow of water into electricity. This energy is then distributed through the national grid to homes, factories, and businesses.
With continued upgrades, such as the Tarbela 5th Extension Project, the power capacity is expected to reach even higher levels in the coming years.
This clean energy production reduces Pakistan’s dependence on fossil fuels and helps lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Irrigation and Agriculture Benefits
Agriculture is the backbone of Pakistan’s economy. The Tarbela Dam plays a major role in supporting this sector by storing water during the summer and releasing it when needed.
The dam’s water helps irrigate millions of acres of farmland across Punjab and Sindh. This ensures stable crop production, even during dry seasons.
Thanks to Tarbela, crops like wheat, rice, cotton, and sugarcane continue to thrive and sustain millions of farmers.
Flood Control and Water Regulation
Pakistan often faces heavy monsoon rains that can lead to dangerous floods. The Tarbela Dam helps manage and control this water flow by storing excess river water.
During peak rainfall, the dam reduces the risk of flooding in downstream areas, protecting cities, villages, and farmland.
This flood control capacity saves lives and prevents large-scale property damage every year.
Engineering Significance
The engineering design of Tarbela Dam is a masterpiece of modern civil engineering. Building an earth-filled dam of this size required advanced planning, material testing, and construction techniques.
Engineers had to manage challenges such as river diversion, sediment control, and stability under pressure.
The project’s success inspired future hydropower developments in Pakistan, such as Mangla Dam and Diamer-Bhasha Dam.
Tarbela continues to be a training and research site for engineers studying dam construction and water management.
Environmental and Social Impact
While the dam provides many benefits, it has also caused some environmental and social challenges.
When Tarbela was built, thousands of people living in nearby villages had to be relocated. The government provided compensation and resettlement programs for the affected families.
Over time, the reservoir has also experienced sedimentation, reducing its water storage capacity. However, several rehabilitation projects are ongoing to improve the dam’s performance and extend its lifespan.
Despite these challenges, the overall impact of Tarbela Dam remains highly positive for Pakistan’s development.
Economic Importance
The Tarbela Dam supports Pakistan’s economy in several ways. It helps reduce the country’s import bill by producing affordable hydropower instead of costly imported fuel.
The continuous water supply from the dam boosts agricultural exports and food security. Additionally, the dam creates thousands of jobs during construction, operation, and maintenance.
It also supports industries that depend on stable power supply and irrigation, making it a vital part of Pakistan’s long-term economic growth.
Future of Tarbela Dam
To maintain its performance, several extension projects have been launched. The Tarbela 4th and 5th Extension Projects aim to add more power-generating units, improve efficiency, and increase capacity.
These projects are expected to generate additional electricity without building a new dam, which makes them cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
By adopting new technologies, Pakistan ensures that Tarbela Dam continues to serve future generations.
Conclusion
The Tarbela Dam is more than just a structure it is a lifeline for Pakistan. It provides water for farming, electricity for homes and industries, and protection from floods.
Since its completion in 1976, it has remained a symbol of engineering excellence and national progress. With continued upgrades and maintenance, Tarbela Dam will keep powering Pakistan’s growth for decades to come.
FAQs
1. Where is Tarbela Dam located?
Tarbela Dam is located on the Indus River in the Haripur District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.
2. When was Tarbela Dam completed?
Construction was completed in 1976, and it began operations the same year.
3. What is the main purpose of Tarbela Dam?
It was built for irrigation, electricity generation, and flood control.
4. How much power does Tarbela Dam generate?
It generates more than 4,800 megawatts (MW) of electricity, making it one of the largest hydropower plants in the world.
5. Why is Tarbela Dam important for Pakistan?
It supports agriculture, provides renewable energy, and protects against floods, contributing greatly to Pakistan’s economy and infrastructure.